Get to know MK UWB Kit Robotics, a solution developed by MobileKnowledge, which brings robot spatial awareness to the next level!
Nowadays, robots can be found in many different sectors, such as private households, commercial locations, warehouses, and medical settings. They either work autonomously or they work side-by-side with us to help us perform our tasks.
Improving spatial awareness in robotics applications can be very challenging, but nonetheless critical to support robot’s operation. In fact, robot’s functionalities and capabilities have evolved recent years: new applications and use cases have appeared, and robots now need to travel autonomously and interact with people in many different ways.
At MobileKnowledge, we have developed a solution, MK UWB Kit Robotics, which brings robot spatial awareness to the next level thanks to the outstanding ranging accuracy and precision offered by Ultra-Wideband (UWB) technology:
- It improves the ability of the robot to position itself in the environment and interact in an effective way with other robots or humans.
- It is flexible and easy to integrate. A Plug & Play solution that can be adapted to the most common robotic use cases and applications.
- A cost-effective solution compared to other positioning solutions.
- Highly accurate and precise position data even in indoor and challenging environments.
Let’s have a first look at the markets and use cases MobileKnowledge is addressing with MK UWB Kit Robotics.
According to Statista1, the total robotics market revenue is projected to reach around 37.37 billion USD in 2023, a market dominated by service robotics (around 75% of the revenue). This large market is shaped by several trends such as Industrial Internet of Things, edge computing, 5G, AI and smart mobility and driven by various applications such as household/social robots, Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), collaborative robots (Cobots) and drones.
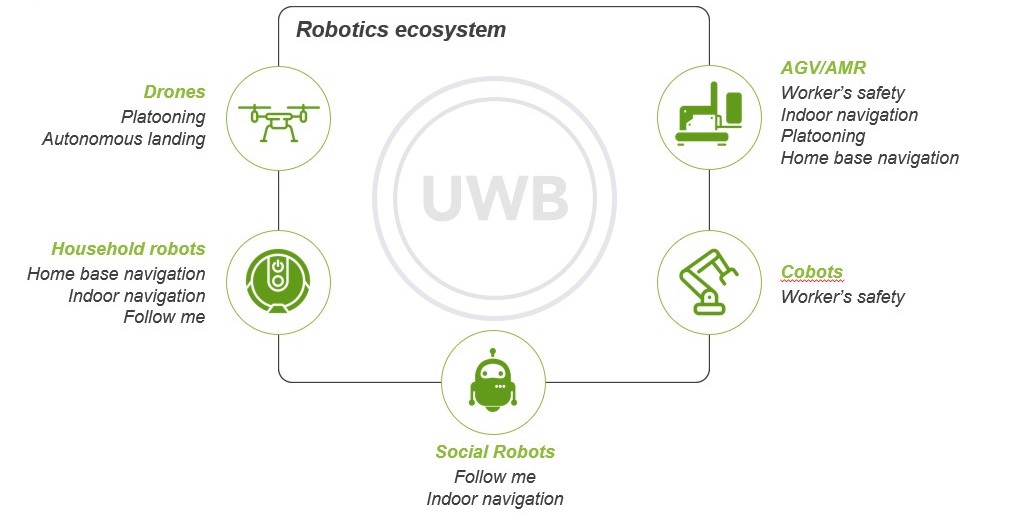
MK UWB Kit Robotics use cases
The MK UWB Kit Robotics developed by MobileKnowledge allows users to easily leverage on UWB technology to bring accurate and precise spatial awareness to the most common robotics use cases:
- Follow me: in this use case robots need to follow a human or another robot as they move in the operating environment. Integrating this capability is critical for personal assistance robots or for heavy loads moving in industrial environments.
- Home base navigation: in this use case the robot needs to autonomously navigate to a specific location or to a home base station. For example, it can return to its charging station when it runs out of battery or to the storage room after completing a task.
- Indoor navigation: to perform the tasks assigned, robots need to position themselves relative to the environment and navigate autonomously to one or more target locations in household or industrial environments. In indoor environments, where GPS cannot be used, UWB provides scalable, real-time and accurate positioning technology which can be used by robots to know exactly where they are at each moment.
- Autonomous landing: flying robots, or drones, are expected to work autonomously. Critical to this task is their ability to land with precision on a static or moving platform. This enables use cases such as payload delivery in logistics, hover and land on indoor ground stations and Drone-in-a-Box use cases.
- Platooning: robots may need to work together, have a leader to lead them, or even work in specific formations to achieve a goal. This has huge applications in warehouse multi-payload delivery, flying cellular networks and entertainment (e.g., aerial shows for drones).
- Worker’s safety: safety is of utmost importance when workers are operating close to dangerous robots or machinery. Robots can detect nearby workers and act appropriately if safety conditions are not met; for example by stopping operation in case a worker is detected in a dangerous area or by always keeping a robot at a safe distance from nearby workers.
All these use cases are supported by MK UWB Kit Robotics. This solution allows users to enable and configure all abovementioned use cases through a Plug & Play UWB Subsystem that transparently adds UWB fine-ranging capabilities to any robotic application. The UWB subsystem can be easily programmed and configured through a simple, but powerful API. Thanks to MobileKnowledge UWB subsystem for robotics, users can add high precision spatial awareness to autonomous robots even in challenging
environments (low/no visibility, high density, indoor). With MK UWB Kit Robotics, you can expect a high level of accuracy and precision, both in distance measurement and angle measurement:
- Accuracy: ± 5 cm (distance measurement), ± 1º (angle measurement)
- Precision: ± 7 cm (distance measurement); ± 4º (angle measurement)
Moreover, MobileKnowledge has developed a set of example applications to demonstrate how to integrate the UWB Subsystem in the most common robot operating systems (ROS2, PX4, etc.). For example, the Follow Me application and the Home-base navigation application integrate the UWB subsystem in ROS2 and demonstrate its operation using the iRobot Create 3 development platform. You can see the use cases in action here.
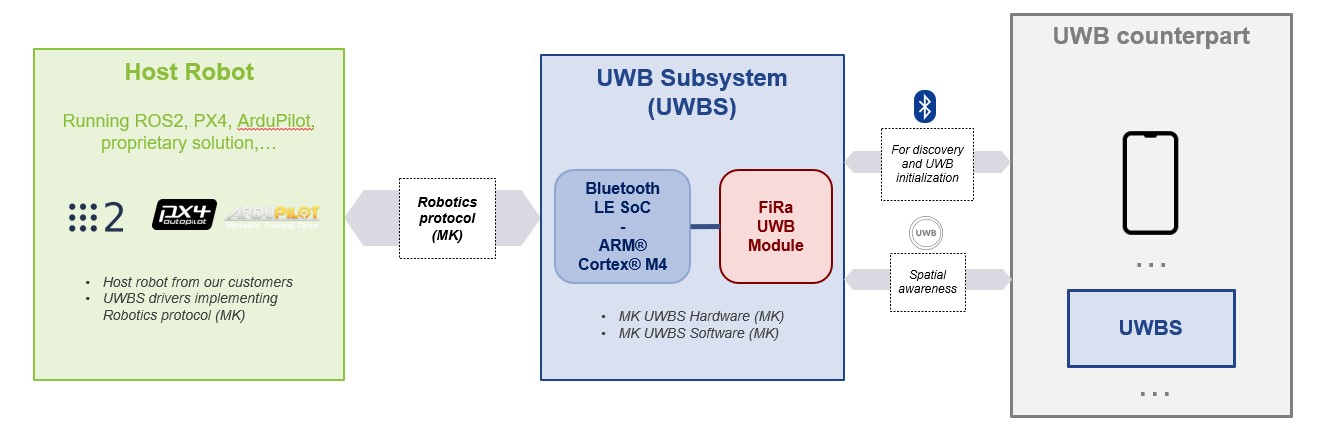
MK UWB Kit Robotics high level architecture
The core of MK UWB Kit Robotics consists of a UWB Subsystem (UWBS) whose hardware and software have been specifically designed by MobileKnowledge to guarantee optimal UWB performance and easy integration in robotics applications and use cases.
The UWBS consists of a Bluetooth LE System on Chip (SoC) that controls the FiRa-certified UWB module (Murata Type 2BP featuring NXP Trimension SR150). It integrates MK UWB 3D antenna board supporting 2D and 3D Angle of Arrival (AoA) measurements. The UWBS can be connected through a serial interface to the host robot running any of the most common operating systems (ROS2, PX4, etc.) or even custom proprietary solutions.
Through a simple, but powerful API (MK Robotics Protocol), it is possible to control the UWBS from the host robot. The UWBS takes care of discovering nearby devices and negotiating the UWB session parameters. All of this is done in a transparent way to the host robot: through Bluetooth LE the UWBS discovers nearby UWB counterpart devices (UWB-compatible Android and iOS mobile phones, UWB tags, other UWBSs) and, upon connection, negotiates all parameters required to initialize the UWB ranging session. As soon as the UWB ranging session is established, the host robot starts receiving UWB ranging notifications with distance and angle information that can be used to implement any spatial-aware robotic application. The UWBS can be set up for any use case using just a few API calls, with the possibility to fine tune the configuration should the use case require it.
Did we catch your attention? If you think MK UWB Kit Robotics is a good fit for your robot applications and use cases, feel free to get in touch with MobileKnowledge for additional information and personalized assessment!
Related topics